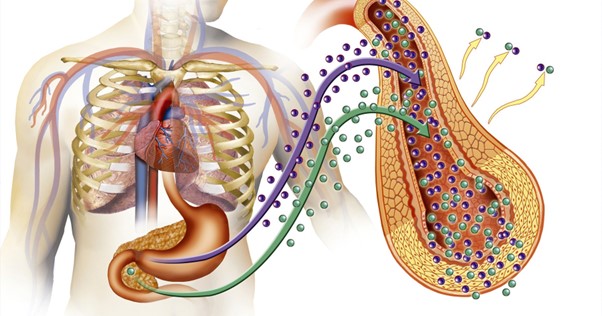
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide, and managing it effectively is crucial for maintaining overall health. While diet, exercise, and medication play significant roles in diabetes management, hormones also have a profound impact on blood sugar levels and overall control of the disease. Understanding the relationship between hormones and diabetes can help individuals better manage their condition and make informed decisions about their health.
Understanding Hormones and Their Role in Diabetes
Hormones are chemical messengers produced by glands in the endocrine system. They regulate various bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, and mood. In diabetes, certain hormones play critical roles in controlling blood sugar levels:
Insulin: Produced by the pancreas, insulin is the hormone most closely associated with diabetes. It helps cells absorb glucose from the bloodstream, thereby lowering blood sugar levels. In type 1 diabetes, the body does not produce insulin, while in type 2 diabetes, the body becomes resistant to insulin’s effects.
Glucagon: Another hormone produced by the pancreas, glucagon works in opposition to insulin. It signals the liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream, raising blood sugar levels. Proper balance between insulin and glucagon is essential for stable blood sugar levels.
Cortisol: Known as the stress hormone, cortisol can influence blood sugar levels. During times of stress, cortisol levels rise, which can increase blood glucose levels. Chronic stress and high cortisol levels can contribute to poor diabetes control.
Adrenaline: Produced by the adrenal glands, adrenaline is released during the “fight or flight” response. It can temporarily increase blood sugar levels to provide quick energy. Frequent spikes in adrenaline due to stress or anxiety can impact diabetes management.
Thyroid Hormones: The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism. Imbalances in thyroid hormones, such as in hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, can affect blood sugar control and overall diabetes management
Hormonal Imbalances and Diabetes Management
Hormonal imbalances can significantly impact diabetes control. Here’s how:
- Insulin Resistance: In type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance occurs when cells become less responsive to insulin. This can lead to higher blood sugar levels and may be influenced by hormonal changes related to obesity, stress, or other factors.
- Stress and Cortisol Levels: Chronic stress elevates cortisol levels, which can lead to insulin resistance and higher blood sugar levels. Managing stress through techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and exercise can help improve diabetes control.
- Menstrual Cycle and Pregnancy: Hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle and pregnancy can affect blood sugar levels. Women with diabetes may experience changes in insulin sensitivity throughout their menstrual cycle and should monitor their blood sugar levels closely.
- Thyroid Disorders: Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) can impact blood glucose levels. Regular monitoring and treatment of thyroid disorders are essential for effective diabetes management.
Strategies for Managing Hormonal Impacts on Diabetes
To manage the impact of hormones on diabetes control, consider the following strategies:
- Monitor Blood Sugar Regularly: Frequent monitoring helps identify patterns and fluctuations in blood sugar levels related to hormonal changes. This information can guide adjustments in medication, diet, and lifestyle.
- Manage Stress Effectively: Incorporate stress-reducing practices into your routine, such as exercise, relaxation techniques, and adequate sleep. Reducing stress can help lower cortisol levels and improve overall diabetes control.
- Stay Informed About Hormonal Changes: For women, understanding how hormonal changes related to the menstrual cycle or pregnancy can affect blood sugar levels is crucial. Consult with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized management plan.
- Regular Check-Ups: Regular visits to healthcare professionals can help manage both diabetes and any hormonal imbalances. Thyroid function tests and stress management strategies should be part of a comprehensive diabetes care plan.
- Balanced Diet and Exercise: A healthy diet and regular physical activity support overall hormone balance and improve insulin sensitivity. Incorporate a balanced diet with whole foods and engage in regular exercise to maintain hormonal health.
Conclusion
Hormones play a crucial role in managing diabetes, and understanding their impact can lead to better control of blood sugar levels. By monitoring hormonal fluctuations, managing stress, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, individuals with diabetes can improve their overall health and effectively manage their condition.